How Solar Electric Technology Works
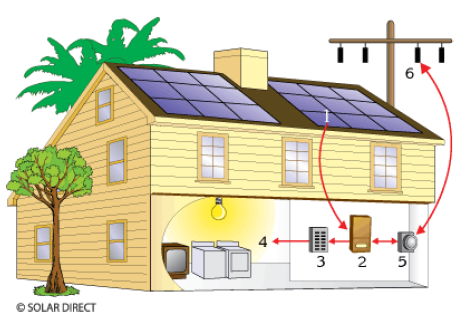
Image above shows a residential Grid-Connected Photovoltaic System.
1. solar panels 2. inverter 3. breaker box 4. home power and appliances
5. meter 6. utility power grid.
(1) Solar Electric or PV modules convert sunlight to electricity. The PV modules generate DC electricity - or direct current - sending it to the inverter. (2) The inverter transforms the DC power into AC electricity for ordinary household needs. (3) Existing electrical panel distributes solar electricity and utility power to (4) loads (appliances). For systems with a battery backup (optional), the inverter also regulates the charge of batteries. The electricity stored in the batteries can be used at night or during blackouts.
A valuable feature of photovoltaic systems is the ability to connect with the existing power grid which allows owners to sell excessive electricity back to the utility with a plan known as (5) Net Metering. At times when you are not using all of the electricity produced by your system, your meter will spin backwards selling the electricity back to the (6) utility power grid at retail rate.

Types of PV Systems
Systems are generally classified according to their functional and operational requirements, their component configuration, and how the equipment is connected to the other power sources and electrical loads (appliances).
Utility Intertie PV Systems (Grid-Connected)
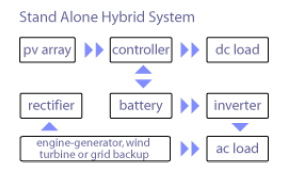
Stand-Alone Solar Electric Systems
Typical PV System Components
PV Power generation systems are made up of interconnected components, each with a specific function. One of the major strengths of PV systems is modularity. As your needs grow, individual components can be replaced or added to provide increased capacity. The selected components will vary depending on the applications, what follows is a brief overview of the components of a typical Solar Electric PV system.
Net Metering
In more than 35 states, customers who own PV systems can benefit from laws and regulations that require "net" electric meter reading. The customer is billed for the net electricity purchased from the utility over the entire billing period-that is, the difference between the electricity coming from the power grid and the electricity generated by the PV system. Through net metering, the customer obtains the full retail electricity rate-rather than the much lower wholesale rate-for kilowatt-hours of PV- produced electricity sent to the utility power grid. The benefits of net metering to consumers are especially significant in areas such as Hawaii and New York, which have high retail electric rates. Utilities also benefit because the solar-generated energy often coincides with their periods of "peak" demand for electricity.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Electric
›› Grid-Tie Solar Electric Systems
›› Grid-Tie Solar Electric Systems with Battery Backup
›› Off-Grid Stand Alone Systems
›› Individual Solar Electric Components
›› Advantages of Photovoltaic Solar Power
›› Other Solar Electric Products and small devices

Grid-Tie Solar Systems (GTS)
A valuable feature of grid-tie or grid-connected photovoltaic systems is the ability to connect with the existing power grid and sell excessive electricity back to the utility with a plan known as Net Metering. At times when you are not using all of the electricity produced by your system, your meter will spin backwards selling the electricity back to the grid at retail rate. This systems do not include a battery. Power is obtained from the utility grid when the system is not producing electricity.

|
|
Grid-Tie Systems with Battery Backup (GTB)
Grid-Tie Solar Electric Systems with Battery Backup have all the features of the Grid-Tie Systems with the addition of a Battery. The battery can store power for use when the system is not producing electricity such as during the night or during blackouts.

|
|
Off-Grid Stand Alone Systems
Off-grid stand alone systems operate independent of the electrical grid. You can purchase individual components to build your own system or purchase pre-packaged systems (pre-packaged systems coming soon).
Solar Electric Individual Components
Build-Your-Own. You can create your own system by purchasing components separately. Photovoltaic systems are modular, you can start with a small system to power small appliances and grow your system as needed or as finances allows and grow to full energy independence.

|
|
Advantages of Photovoltaic Solar Power
Photovoltaic solar power is one of the most promising renewable energy sources in the world. Compared to nonrenewable sources such as coal, gas, oil, and nuclear, the advantages are clear:
| • | Generates free energy from the sun |
| • | Has no moving parts to break down thus requiring minimal maintenance |
| • | Non-polluting energy reduces emissions: Has no direct impact on the environment |
| • | Photovoltaic (PV) cells are modular, you can start with a small system and expand as your needs increase |
| • | Systems have a long life & durability. Cells last 25-30 years |
| • | Grid-Tie systems allow you to sell excess electricity back to the utility |
| • | Can be installed and operated anywhere including areas of difficult access and remote locations |
| • | Helps get us off dependence on foreign oil |
| • | PV cells make no noise and give off no exhaust |
| • | Allow the use of electricity in remote areas where it would be expensive or impossible to run power lines |
| • | Have electrical power during blackouts |
| • | Rebates and incentives available. 30% Federal tax credit, plus state and local incentives |

Sunlight to Electricity
Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight into electricity and is emerging as a major power source due to its numerous environmental and economic benefits and proven reliability.
Enough free sunlight falls on earth to supply our energy needs for years to come.
Environmental Benefits: As PV generates electricity from light, PV produces no air pollution or hazardous waste. It doesn't require liquid or gaseous fuel to be transported or combusted.
Economic and Social Benefits: Sunlight is free and abundant. Photovoltaic systems allows you to generate electricity and store it for use when needed. Photovoltaic contributes to our energy security, as a young technology, it creates jobs and strengthens the economy. It frees us from uncertainties and foreign oil dependence.
This energy source is free, clean and highly reliable. PV systems are long-lasting and require little maintenance. The benefits of Photovoltaics far outweigh the initial cost the systems.
Photovoltaic System
A complete system includes different components that should be selected taking into consideration your individual needs, site location, climate and expectations. In this section we review the components' funtion and several different system types.

Major System Components
The functional and operational requirements will determine which components the system will include. It may include major components as; DC-AC power inverter, battery bank, system and battery controller, auxiliary energy sources and sometimes the specified electrical loads (appliances).
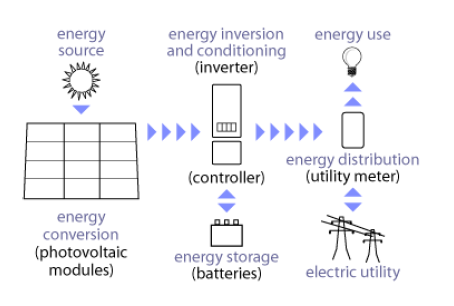
PV Modules - convert sunlight instantly into DC electric power.
Inverter - converts DC power into standard AC power for use in the home, synchronizing with utility power whenever the electrical grid is distributing electricity.
Battery - stores energy when there is an excess coming in and distribute it back out when there is a demand. Solar PV panels continues to re-charge batteries each day to maintain battery charge.
Utility Meter - utility power is automatically provided at night and during the day when the demand exceeds your solar electric power production.
The utility meter actually spins backwards when solar power production exceeds house demand, allowing you to credit any excess electricity against future utility bills.
Charge Controller - prevents battery overcharging and prolongs the battery life of your PV system.
In addition, an assortment of balance of system hardware; wiring, overcurrent, surge protection and disconnect devices, and other power processing equipment.
System Sizing
The size of the PV system that will meet your expectations depends on your individual needs, site location and climate. Please contact us and our engineers and consultants will prepare a customized system quote.
The modular design of PV panels allows the systems to grow and change as system needs change and grow. You can start with our storm outage backup system Starter Kit, an all-in-one entry level solar photovoltaic package, and then grow into full independence!
Types of PV Systems
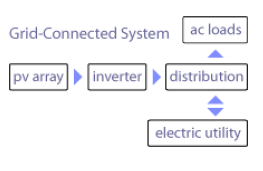
Grid Connected
Grid-connected or utility-intertie PV systems are designed to operate in parallel with and interconnected with the electric utility grid. The primary component is the inverter, or power conditioning unit (PCU). The inverter converts the DC power produced by the PV array into AC power consistent with the voltage and power quality required by the utility grid. The inverter automatically stops supplying power to the grid when the utility grid is not energized. A bi-directional interface is made between the PV system AC output circuits and the electric utility network, typically at an on-site distribution panel or service entrance. This allows the power produced by the PV system to either supply on-site electrical loads, or to back feed the grid when the PV system output is greater than the on-site load demand. During periods when the electrical demand is greater than the PV system output (night-time), the balance of power required is received from the electric utility This safety feature is required in all grid-connected PV systems, it also ensures that the PV system will not continue to operate and feed back onto the utility grid when the grid is down for service or repair.
Stand Alone System
Stand-alone PV systems are designed to operate independent of the electric utility grid, and are generally designed and sized to supply certain DC and/or AC electrical loads. Stand-alone systems may be powered by a PV array only, or may use wind, an engine-generator or utility power as a backup power source in what is called a PV-hybrid system. The simplest type of stand-alone PV system is a direct-coupled system, where the DC output of a PV module or array is directly connected to a DC load.
Since there is no electrical energy storage (batteries) in direct-coupled systems, the load only operates during sunlight hours, making these designs suitable for common applications such as ventilation fans, water pumps, and small circulation pumps for solar thermal water heating systems. Matching the impedance of the electrical load to the maximum power output of the PV array is a critical part of designing wellperforming direct-coupled system. For certain loads such as positive-displacement water pumps, a type of electronic DC-DC converter, called a maximum power point tracker (MPPT) is used between the array and load to help better utilize the available array maximum power output.
In many stand-alone PV systems, batteries are used for energy storage. Below is a diagram of a typical stand-alone PV system with battery storage powering DC and AC loads.
Below is a diagram of a Photovoltaic Hybrid System with battery storage powering DC and AC loads and using a using a backup power source (wind, engine-generator or utility power)
Solar PV Electric
Grid-Interconnected Solar System with Battery Storage
Start with a Storm Outage Back-up System...

...Grow into Full Energy Independence!
| • | Peace of Mind |
| • | Energy Independence |
| • | Environmentally Responsible |
Enough sunlight hits the United States each day to provide for the entire world's electricity needs. Taking advantage of this clean, renewable and highly available resource could put Americans in control of their electrical needs. While devastating storms will continue to ravage the country, Americans could potentially avoid the electrical blackouts left in their wake.
Coming to the aid of home-owners seeking both lower monthly bills and reliable home power solutions, Solar Direct offers consumers the Solar Freedom™ Package Starter Kit, an All-In-One entry-level solar photovoltaic (PV) package, combining immediate power backup, regular monthly utility savings and the long-term ability to grow the home solar system into complete energy-independence.
▪ Benefits of PV Power Systems
| • | Solar power systems lower your utility bills and insulate you from utility rate hikes and price volatility due to fluctuating energy prices |
| • | Solar increases property value and home resale opportunities |
| • | Purchase of a solar power system allows you to take advantage of available tax and financial incentives |
| • | Solar electric systems are quiet, reliable, fossil-fuel free |
| • | Unlike mobile power generators, avoids Greenhouse gas emissions |
▪ Base Product Components
Photovoltaic Panels
A 3 panel system consisting of 550 watt-hours sufficient for running select home appliances in "survival mode".
PS1-3000 Inverter
| • | Solar power systems lower your utility bills and insulate you from utility rate hikes and price volatility due to fluctuating energy prices |
| • | Solar increases property value and home resale opportunities |
| • | Purchase of a solar power system allows you to take advantage of available tax and financial incentives |
| • | Solar electric systems are quiet, reliable, fossil-fuel free |
| • | Unlike mobile power generators, avoids Greenhouse gas emissions |
| • | 3000VA Vented Inverter |
| • | Battery-based Power Back-up - AGM Batteries |
| • | MX60 Charge Controller |
| • | True Sinewave Output |
| • | CEC certified 91% Efficiency Inverter |
| • | Zero AC Watts Consumed at Night |
| • | Proven Maximum Power Point Tracking |
| • | 16 Millisecond AC Transfer Switch |
| • | Type 3R Rainproof Enclosure |
| • | Multiple Anti-Islanding Safeguards |
| • | Standard 5-year Warranty |
PS1-3000 Complete Details

1. SOLAR PV PANELS convert sunlight instantly into DC electric power. With a PV (photovoltaic) system, your home will operate even during a utility power outage.
2. INVERTER converts DC power into standard AC power for use in the home, synchronizing with utility power whenever the electrical grid is distributing electricity
3. BATTERIES (included in the Inverter) provide power during a utility outage. Solar PV panels continues to re-charge batteries each day to maintain battery charge.
4. UTILITY POWER is automatically provided at night and during the day when the demand exceeds your solar electric power production. Utility meter actually spins backwards when solar power production exceeds house demand, allowing you to credit any excess electricity against future utility bills.
5. HOUSE BREAKER BOX Existing electrical panel distributes solar electricity and utility power to loads (appliances) in the house.
6. HOME APPLIANCES watt usage varies. Based on a 6 sun hours per day of sun, a Solar Freedom Starter Kit™ can supply: Refrigerator 500 watts 5 hrs, TV 150 watts .75 hr, Light Bulb 60 watts 1 hr, Radio 1 watt 10 hrs, Microwave 600 watts .25 hr
▪ How does it Work?
The Solar Freedom™ Starter Kit converts sunlight into DC electricity through the use of solar panels (PV Modules). From there, the DC electricity is fed through the inverter which transforms it into utility-grade AC electricity to power your home. Sometimes, your home will require more electricity than the system provides and the excess need is filled by the utility company. However, when less electricity is required than the system is generating, the excess can be fed (or sold) back to the utility. In the event of a blackout, the Solar Freedom™ Starter Kit relies on its unique battery back-up to continue to provide minimal electricity to your home.
Part or the entire household load is powered via the inverter connected to the existing household circuit breaker box. Typically, heavy energy consumption devices such as air-conditioners, electric heating, electric stoves, heat pumps and electric hot water heaters are left running directly on the utility power. These devices are seen as non-critical during a utility outage due to their high instantaneous power and daily energy consumption, placing a huge burden on the system inverter and energy storage battery bank during a utility failure. In the event of a utility power outage, power will be lost to the "big", non-critical loads. At the same time, the inverter will take over supply to the “dedicated” loads, supplying with power until the utility power is restored.
▪ What Does It Do?
The Solar Freedom™ Starter Kit is able to run your home in "critical mode" for approximately 3 days during a storm or other electrical outage. For example, the Solar Freedom Starter Kit can run an energy-efficient refrigerator for 24 hours/day, keeping your food fresh. It can simultaneously run a TV for 45 minutes/day and a clock radio for 10 hours, keeping your family in communication with the world. In addition, a microwave over can be run for 15 minutes, providing your family with 2-3 hot meals.
During normal operating periods, the system will continue to provide your home with excess energy even when the electric companies get back online. This will allow you to continually keep monthly utility bills under control. The table below demonstrates typical home appliances that can be supported by Solar Freedom™ when running the home in "power outage" survival mode. As the system is upgradeable, more solar modules (and home appliance support) can be added over time, to support up to 3000 Watts of electricity usage per day.
Example Appliance "Critical Use" Patterns Supported by the base Solar Freedom™ Starter Kit (550 Watts of solarbased electricity)*
| Primary Usage Appliance | Average Watts | Usage 1 (hrs/day) | Usage 2 (hrs/day) |
| Standard Refrigerator | 500 | 24 hours** | |
| Energy-Efficient Refrigerator (SunFrost) | 150 | 24 hours*** | |
| 25-inch color TV | 150 | 45 minutes | 7 hours |
| One lamp | 60 | 1 hour | 10h hours |
| Clock radio | 1 | 10 hours | 10 hours |
| Small Microwave Oven | 600 | 15 min | 15 min |
*Appliances and usage time varies; table based on 6 sun hours per day. Battery backup without the sun averages 3 days.
**Standard refrigerator use based on a reduced operating temperature during power outages; performance can be increased by making ice blocks before outage for thermal storage.
***SunFrost super-efficient refrigerator operating under normal conditions.